Scientific Materials
Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Learners of Cellular Morphology
TUPELO Trial: A Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Evaluate Efficacy, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of REC-4881 in Subjects With Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP): Study Design
High-Resolution Genome-Wide Mapping of Chromosome-Arm-Scale Truncations Induced by CRISPR-Cas9 Editing
A Phenomics Platform Combining Imaging and Artificial Intelligence for Rapid Validation and Advancement of Novel Oncology Targets
Biological Cartography: Building and Benchmarking Representations of Life
Multi-Objective GFlowNets
MolE: A Molecular Foundation Model for Drug Discovery
Obtaining Cellular Morphological Embeddings Across Experimental Batches
POPLAR-NF2: A Parallel-Group, Two-Staged, Phase 2/3, Randomized, Multicenter Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of REC-2282 in Participants With Progressive NF2-Mutated Meningiomas
Identification and Optimization of Novel Small Molecule Modulators of Immune Checkpoint Resistance with a Unified Representation Space for Genomic and Chemical Perturbations
Mapping Biology with a Unified Representation Space for Genomic and Chemical Perturbations to Enable Accelerated Drug Discovery
WILDS: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shifts
Functional Immune Mapping with Deep-Learning Enabled Phenomics Applied to Immunomodulatory and COVID-19 Drug Discovery
Identification of Potential Treatments for COVID-19 through Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Phenomic Analysis of Human Cells Infected with SARS-CoV-2
Cell Painting, a High-Content Image-Based Assay for Morphological Profiling Using Multiplexed Fluorescent Dyes
A New Phenotypic Lexicon for Accelerated Translation
Strategy for Identifying Repurposed Drugs for the Treatment of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation
Scientific Materials
Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Learners of Cellular Morphology
Sep 27, 2023
|
arXiv
|
Pipeline
TUPELO Trial: A Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Evaluate Efficacy, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of REC-4881 in Subjects With Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP): Study Design
May 6, 2023
|
11th Annual Clinical Cancer Genetics and Genomics Conference
|
Pipeline
High-Resolution Genome-Wide Mapping of Chromosome-Arm-Scale Truncations Induced by CRISPR-Cas9 Editing
Apr 18, 2023
|
bioRxiv
|
Platform
A Phenomics Platform Combining Imaging and Artificial Intelligence for Rapid Validation and Advancement of Novel Oncology Targets
Apr 17, 2023
|
AACR Annual Meeting
|
Platform
Biological Cartography: Building and Benchmarking Representations of Life
Dec 9, 2022
|
Learning Meaningful Representations of Life (LMRL) Workshop at NeurIPS
|
Partnership
Multi-Objective GFlowNets
Dec 2, 2022
|
AI for Accelerated Materials Design (AI4Mat) Workshop at NeurIPS
|
Platform
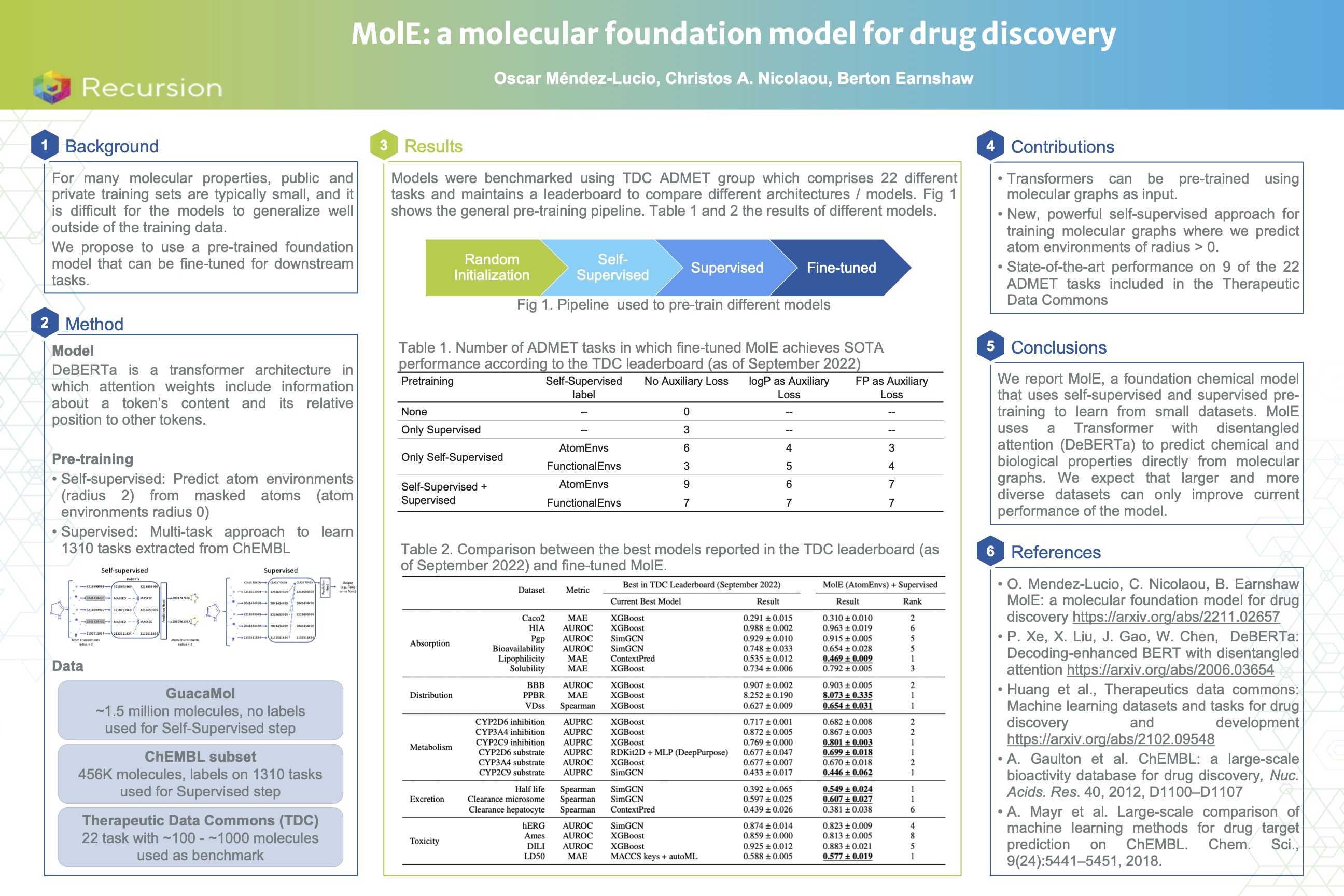
MolE: A Molecular Foundation Model for Drug Discovery
Nov 8, 2022
|
Learning Meaningful Representations of Life (LMRL) Workshop at NeurIPS
|
Platform
Obtaining Cellular Morphological Embeddings Across Experimental Batches
Oct 18, 2022
|
CytoData Symposium
|
Platform
POPLAR-NF2: A Parallel-Group, Two-Staged, Phase 2/3, Randomized, Multicenter Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of REC-2282 in Participants With Progressive NF2-Mutated Meningiomas
Jun 19, 2022
|
NF Conference
|
Pipeline
Functional Immune Mapping with Deep-Learning Enabled Phenomics Applied to Immunomodulatory and COVID-19 Drug Discovery
Aug 20, 2020
|
bioRxiv
|
Platform
Identification of Potential Treatments for COVID-19 through Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Phenomic Analysis of Human Cells Infected with SARS-CoV-2
Apr 23, 2020
|
bioRxiv
|
Platform
Cell Painting, a High-Content Image-Based Assay for Morphological Profiling Using Multiplexed Fluorescent Dyes
Aug 25, 2016
|
Nature Protocols
|
Platform
A New Phenotypic Lexicon for Accelerated Translation
Jan 20, 2015
|
Circulation
|
Platform
Strategy for Identifying Repurposed Drugs for the Treatment of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation
Dec 8, 2014
|
Circulation
|
Pipeline
WILDS: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shifts
Jun 30, 2021
|
International Conference on Machine Learning
|
Platform
Identification and Optimization of Novel Small Molecule Modulators of Immune Checkpoint Resistance with a Unified Representation Space for Genomic and Chemical Perturbations
Apr 8, 2022
|
AACR Annual Meeting
|
Platform
Mapping Biology with a Unified Representation Space for Genomic and Chemical Perturbations to Enable Accelerated Drug Discovery
Nov 30, 2021
|
NeurIPS Learning Meaningful Representations of Life Workshop
|
Platform
Open Source Data Sharing
We believe in the benefits of open source and open science, and that by releasing open datasets, we drive value for us and society as a whole. Visit www.rxrx.ai to explore our released datasets.
COVID-19
In 2020, we acted boldly to contribute data to the scientific community in hopes it would be useful in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. We partnered with a biosafety level 3 facility to infect a variety of human cells with live SARS-CoV-2 virus, and used our platform to investigate the therapeutic potential of a library of approved drugs. We released our findings as an open-source dataset for the scientific community in April of 2020, which can be downloaded here. Following our initial dataset release, we used our platform to model and screen for therapeutics that can treat the most severe forms of COVID-19 that have progressed to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). We modeled the cytokine storm associated with late-stage COVID-19, treated it with a library of approved drugs, and in August 2020, released the first morphological dataset representing inflammatory effects and potential treatments in the context of COVID-19 ARDS, along with a preprint of our findings.
RxRx Series
We have also released some of the largest open-sourced biological datasets in the world, the RxRx series, under terms that allow for broad academic and non-commercial use. As part of the series, we also released a preprint that demonstrates the capabilities of Recursion’s platform to model complex immune biology and screen for new therapeutics. To explore our released datasets, please visit our website at www.rxrx.ai. Our contribution to a greater understanding of human biology is just as important as the medicines we advance.
Phenom-Beta
We have released the first in a potential series of foundation models for external use (both non-commercial and commercial) hosted on NVIDIA’s BioNeMo platform. We call this model Phenom-Beta. It flexibly processes microscopy images into general-purpose embeddings. In other words, Phenom-Beta can take a series of images and create a meaningful representation of the input image. This enables robust comparison of images, and other data science techniques to decode any biology or chemistry within such images. This allows scientists to systematically relate genetic and chemical perturbations to one another in a high-dimensional space, helping determine critical mechanistic pathways and identify potential targets and drugs. Currently, the model is available through the API and will be available through BioNeMo Beta. Learn more at at www.rxrx.ai.
Want to help us explore the uncharted?
We're working to solve some of the most meaningful problems facing human health today. Come do the most impactful work of your career at a company that prioritizes belonging, collaboration and career development.


.png)



.jpg)

.jpg)


